With the development of today’s society, the sheet metal industry also developed rapidly. Sheet metal now involves all walks of life. For any sheet metal part, it has a certain processing process, that is, the so-called process, to understand the sheet metal processing process, first of all, to know the selection of sheet metal materials.
一. The selection of sheet metal processing materials
Sheet metal and general use of materials are cold-rolled sheet (SPCC), hot-rolled sheet (SHCC), galvanized sheet (SECC, SGCC), copper (CU) brass, red copper, beryllium copper, aluminum (6061, 6063, hard aluminum, etc.), aluminum profiles, stainless steel (mirror surface, wire drawing surface, fog surface), according to the different roles of the product, the selection of different materials, generally from the use of the product and cost to consider.
1. Cold rolled sheet SPCC:
Mainly used in electroplating and paint parts, low cost, easy to form, material thickness ≤3.2mm.
2. Hot rolled plate SHCC:
Material T≥3.0mm, also used electroplating, paint parts, low cost, but difficult to form, mainly used flat parts.
3. Galvanized sheet SECC:
SECC electrolytic plate is divided into N material, P material, N material is not mainly surface treatment, high cost, P Material is used for spraying parts.
4. Copper:
Mainly with conductive materials, its surface treatment is nickel plating, chromium plating, or no treatment, high cost.
5. Aluminum plate:
General surface chromate (J11-A), oxidation (conductive oxidation, chemical oxidation), high cost, silver plating, nickel plating.
6. Aluminum:
Materials with complex cross-section structures are widely used in various boxes. Surface treatment with aluminum plate.
Mainly used without any surface treatment, high cost.
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
二. plate metal processing process
According to the differences in the structure of sheet metal parts, the process can be different, but generally not more than the following points.
1. Blanking:
There are various blanking ways, mainly in the following ways.
①. Shearing machine: is the use of shearing machine shear strip simple materials, it is mainly for mold blanking forming preparation processing, low cost, accuracy is less than 0.2, but can only be processed without holes without cutting Angle strip or block.
②. Punch: is the use of punch in one step or more steps in the plate will be parts of the plate after punching forming various shapes of materials, its advantage is the cost of short hours, high efficiency, high precision, low cost, suitable for mass production, but to design the mold.
③. NC NC blanking, NC blanking first to write numerical control processing program, the use of programming software, will draw the expansion diagram written into NC number pull processing machine tools can identify the program so that according to these programs step by step a knife on the flat plate cutting the shape of the plate, but its structure by the tool structure, low cost, accuracy in 0.15.
④. Laser blanking is the use of laser cutting. In a large plate will be cut out, the structure of the plate shape, the same as NC blanking need to write laser program, it can be a variety of complex shapes of the plate, the cost is high, the accuracy of 0.1.
⑤. Sawing machine: mainly used under aluminum profile, square tube, drawing tube, round bar material, low cost, low precision.
2. The flanging:
Also called a pumping hole, the hole is in a small hole on the smoke into a larger hole, tapping again, mainly with the thickness of thin sheet metal processing, increase the strength and the screw thread turns, avoid sliding tooth, commonly used in thickness is thin, it’s around the normal shallow flanging, basically did not change, the thickness of thin thickness is allowed in the 30-40%, The maximum flanging height can be obtained when the flanging height is 40-60% higher than the normal flanging height. When the plate thickness is larger, such as 2.0 and 2.5, the plate thickness can be tapped directly.
3. Press:
Press is the use of mold forming processing working procedure, general processing of punching and cutting Angle, blanking, punching convex hull (convex point), salt tear, suction hole and forming processing, the processing needs to have the corresponding mold to finish operation, such as punching blanking die, convex BaoMo, tearing mode, pumping hole pattern, forming mold, etc., operating mainly pay attention to the position, direction.
4. Pressure riveting:
Pressure riveting mainly pressures riveting nuts, screws, loose, etc., which is completed by hydraulic pressure riveting machine or punch, riveted to the sheet metal parts, and riveting way, need to pay attention to the direction.
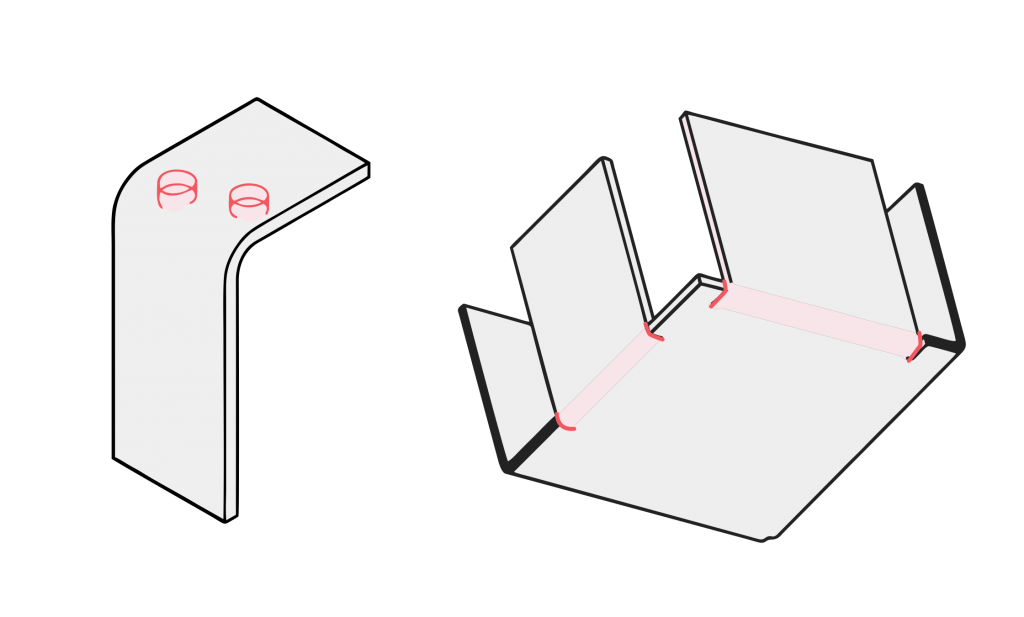
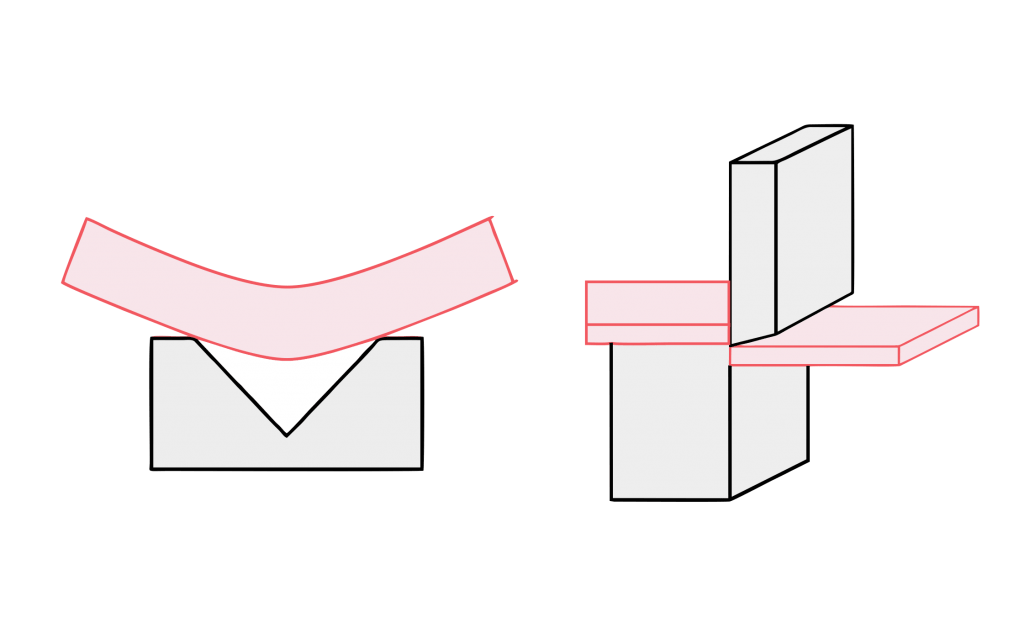
5. Bending;
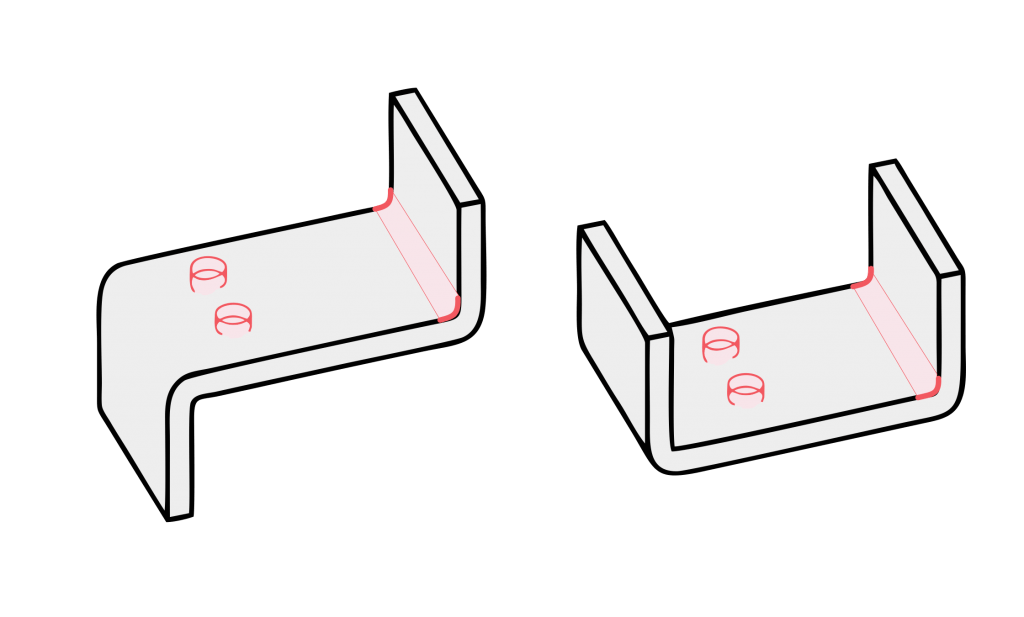
Bending is the folding of 2D flat pieces into 3D parts. Its processing needs to have a folding bed and the corresponding bending mold to complete, and it also has a certain bending order; its principle is that the next knife does not interfere with the first folding and will produce interference after folding.
The number of bending strips is T=3.0mm less than 6 times the plate thickness calculation slot width, such as: T=1.0, V= 6.0 F=1.8, T=1.2, V=8, F=2.2, T=1.5, V=10, F=2.7, T=2.0, V=12, F=4.0
Folding bed mould classification, straight knife, curved knife (80℃, 30℃)
When the aluminum plate is bent, cracks can be increased, and the width of the lower die groove can be increased. (Annealing can avoid cracks).
Note when bending:
① the drawing surface requires the thickness and quantity of the plate;
② bending direction;
③ bending Angle;
④ bending size;
⑤ Appearance, electroplated chrome materials are not allowed to have creases.
Bending and pressure riveting process relationship, under normal circumstances first after bending pressure, but there will be interference after material pressure riveting is about to fold first after pressure, and some need to bend – pressure riveting – bending and other processes.
6. The welding
Welding definition: the atoms and molecules of the material to be welded form an integral whole from the lattice distance of Jingda.
① Classification: A fusion welding: argon arc welding, CO2 welding, gas welding, manual welding B pressure welding: spot welding, butt welding, bump welding C brazing: electric chromium welding, copper wire.
② Welding mode: A CO2 gas shielded welding b argon arc welding C spot welding d robot welding.
The selection of welding mode is according to the actual requirements and material. Generally, SPEAKING, CO2 shielded welding is used for iron plate welding. Argon arc welding for stainless steel, aluminum plate welding, and robot welding can save time, improve work efficiency and welding quality, and reduce work intensity.
③ Welding defect and its prevention
Spot welding strength is not enough to play convex points, impose CO2 welding area, high productivity, less energy consumption, low cost, strong ability to resist rust Argon arc welding: dissolve depth, dissolves slow, low efficiency, high production cost, a tungsten inclusion defects, but had many advantages, such as the welding quality is good, can be welding of nonferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, etc.
④ Welding deformation causes:
Insufficient preparation before welding, need to add the fixture
Welding fixture defective improvement process
Bad welding sequence
⑤ Welding deformation rectification method: flame rectification method, vibration method, hammer method.
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
Categories
Share On
Recent Post
What is Overmolding? A Complete Guide
In today’s manufacturing world, creating durable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing
A Complete Guide on the Types Of Screw Head
You’ve probably stood in front of a confusing display of